Check behind the ears and. Ticks are the most important external parasites commonly found in cattle and are responsible for severe economic losses both through the direct effects of blood-sucking and indirectly as vectors of pathogens for transmission of the spread of disease.
The Ornate Cow Tick Dermacentor reticulatus.
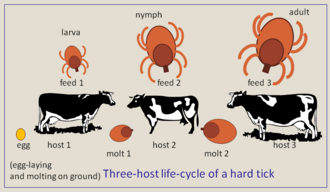
Do ticks affect cows. Its wounds may attract flies which lay their eggs again the larva may be formed. Cattle become infected when they are bitten by infected ticks and the bacterium passes into the bloodstream. Heavy cattle-tick infestation causes tick-worry and blood loss which leads to loss of condition and sometimes death.
This tick is currently only recorded in W Wales NS Devon and Essex mainly in coastal sand dunes and marsh but recently in Essex grassland 5. The ticks can carry parasites that cause cattle fever a significant and often fatal disease in livestock. There are four stages in the life cycle of ticks.
Cattle ticks are found widely in northern Australia from northern parts of Western Australian and the Northern Territory eastern and northern regions of Queensland and into. Hair loss is common when cows with hair have ticks. Also called a.
They can also carry and transmit tick fever organisms which cause illness and death in cattle. Others however can transmit diseases and cause significant production losses resulting in severe welfare concerns if the infestation is not addressed. Injuries or wounds from its bites may lead to a secondary infection.
Larger ticks cause obstructive and painful damage such as Amblyomma variegatum adults which often feed on udders of cattle and reduce suckling by the calves. Anemia is the. Ticks affect milk production in cattle.
Hyalomma truncatum adults feed on the feet of sheep and goats causing lameness. The disease is usually first reported in cattle in May or June when ticks start to become active. Heavy burdens of paralysis ticks are rare and they are usually present in mixed infestations with bush ticks.
It carries canine babesiosis which is a risk to dogs and it is implicated in transmission of Tick-borne Encephalitis TBE. The cattle tick Rhipicephalus microplus is an important external parasite of cattle although other animals such as horses buffalo sheep and camelids can be affected too. There has never been a confirmed case of Lyme disease originating from a tick.
Life History of Ticks. The disease causes anemia rapid breathing weight loss decreased milk production and death. Ous ticks of all stages 10 and thereby divert subadult vector ticks from feeding on reservoir-competent hosts.
Of the infected cattle that have not been exposed to the disease previously 70 to 90 percent die. A simulation model indicated that the availability of incom-petent hosts for subadult tick stages would reduce preva-lence of infection 24. The egg the six-legged.
Each fattened female tick can be responsible for up to 89 mL of milk reduction. The tick also transmits the protozoan Babesia bigemina which causes Texas Cattle fever a devastating disease of the cattle industry. Cattle in the UK are affected by a wide range of ectoparasites.
3 Common Types of Ticks on Cows American Dog Tick. New cases may then continue to appear through to the autumn. Other estimates indicate that losses in milk production reach 23.
Some symptoms of ticks include. The direct effect of ticks on dairy cattle can reduce total milk production by approximately 90 llactationcow. Spinose ear ticks are found in western North America and frequently infest livestock especially cattle and horses.
Tick paralysis can also affect cattle dogs and some other mammals. For more information click here. Cattle tick infestation is a notifiable disease in NSW.
Fortunately the most important tick-borne disease in North America Lyme disease is not present in wild animal populations in Colorado ie not endemic. These are some of the serious diseases caused by ticks or associated with ticks Diseases Humans or animals affected Tick paralysis Mainly sheep and goats Spring lamb paralysis Lambs and sometimes calves Sweating sickness Cattle especially calves Tick-borne diseases Cattle sheep and goats Tick-bite fever Man Tick paralysis Man. Larva or seed tick the nymph and the.
Our observation that questing nymphal and adult ticks collected on a cattle pasture were. The spinose ear tick enjoys taking up residence in the ears of cattle and other livestock. You should see some red or bumpy patches in the skin of your cows with ticks.
If left unchecked this parasite can significantly reduce cattle live-weight gain and milk production. The three main ticks of concern in NSW are the paralysis tick the bush tick and the cattle tick. Information on identifying ticks can be found.
Red Water Fever is caused by the protozoan parasite Babesia divergens. Tick bites also reduce the quality of hides and skins. Some of these are simply nuisance pests affecting grazing patterns and causing mild irritation.
Seen most often east of the Rocky Mountains the American dog tick is a commonly seen tick that. You will notice some parts of their skin are exposed. Ticks produced on wildlife can reinfest treated cattle and they continually pose a problem for Arkansas cattle producers.
Ticks are also capable of transmitting diseases such as anaplasmosis to cattle.
